Samsung TV Screen Mirroring Not Working Windows 10: Troubleshooting Guide
Screen mirroring, the ability to wirelessly display content from a Windows 10 computer onto a Samsung TV, offers convenience for presentations, media consumption, and collaborative efforts. However, users frequently encounter issues preventing successful connection and mirroring. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to troubleshoot common causes when screen mirroring from a Windows 10 computer to a Samsung TV fails. It covers various potential problems and provides systematic solutions to resolve them.
Understanding the technology underpinning screen mirroring is crucial. The most common protocols employed are Miracast and WiDi (Wireless Display, an Intel technology). Miracast is a peer-to-peer wireless screen casting standard, allowing devices to communicate directly without an intermediate network, although being connected to the same Wi-Fi network can sometimes improve stability. Samsung TVs and Windows 10 computers generally support Miracast. The failure of screen mirroring often stems from compatibility issues, driver problems, network configuration errors, or software conflicts.
Ensuring Device Compatibility and System Requirements
Before delving into troubleshooting steps, verifying that both the Samsung TV and the Windows 10 computer meet the minimum requirements for screen mirroring is paramount. A Samsung Smart TV manufactured after 2015 generally supports Miracast. Older models may require a firmware update or may not be compatible at all. Check the TV's user manual or the Samsung support website for specific model information and compatibility details.
On the Windows 10 side, the computer must support Miracast. To confirm this, press the Windows key + P to open the Project sidebar. If "Connect to a wireless display" option is present, the computer likely supports Miracast. However, this does not guarantee full compatibility; further checks are advisable. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator (search for "cmd," right-click, and select "Run as administrator"). Type `dxdiag` and press Enter. This opens the DirectX Diagnostic Tool. In the tool, click "Save All Information" and save the file. Open the saved text file and search for "Miracast." The presence of "Miracast: Available, with HDCP" indicates that the computer's hardware and drivers support Miracast. If Miracast is not listed or indicates an error, proceed to update or reinstall the network adapter drivers.
Furthermore, certain hardware configurations are known to cause issues. Some older graphics cards or wireless adapters may have limited or incomplete Miracast support. Consider updating the drivers for these components from the manufacturer's website (Intel, NVIDIA, AMD) rather than relying solely on Windows Update. A clean driver installation, where older drivers are completely removed before installing the new ones, can be beneficial.
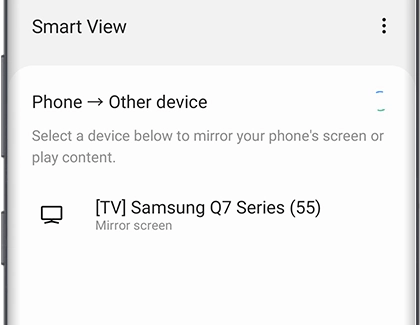
It is also crucial that the TV has Screen Mirroring enabled. This setting is often found in the 'Network' or 'External Device Manager' settings of the TV. Make sure it is set to 'On' or 'Enabled'. Some TVs also offer options to restrict access, such as requiring a PIN. If this is enabled, ensure the correct PIN is entered when prompted on the Windows 10 computer.
Troubleshooting Network Connectivity and Interference
While Miracast is designed to operate independently of a Wi-Fi network, a stable wireless environment is still necessary for optimal performance. Interference from other devices, such as Bluetooth devices, microwave ovens, or other wireless networks, can disrupt the Miracast connection. Ensure that the computer and the TV are in close proximity to each other and away from potential sources of interference.
Even though a direct Wi-Fi connection is established for Miracast, both devices often operate more smoothly when connected to the same Wi-Fi network. This allows for improved communication and reduces the likelihood of conflicting network configurations. Verify that both the Samsung TV and the Windows 10 computer are connected to the same Wi-Fi network. If using a dual-band router (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), try connecting both devices to the 5 GHz band, as it generally offers less interference and higher bandwidth. However, be aware that older devices might not support the 5 GHz band.
Firewall settings on the Windows 10 computer can also interfere with screen mirroring. Windows Firewall or third-party security software might block the necessary communication ports. To address this, temporarily disable the firewall to see if it resolves the issue. If it does, create exceptions in the firewall for Miracast and related services. The specific ports required for Miracast may vary, but generally, allowing inbound and outbound connections for the "Wireless Display" feature in Windows Firewall is a good starting point. Consult the documentation for the security software in use for instructions on creating exceptions.
Furthermore, ensure that the Wi-Fi adapter on the Windows 10 computer is configured correctly. In Device Manager, locate the network adapter, right-click, and select "Properties." In the "Advanced" tab, look for settings related to wireless mode or channel width. Experiment with different settings to see if it improves the connection stability. For example, try setting the wireless mode to "IEEE 802.11n" or "IEEE 802.11ac" if available. Ensure that the channel width is set to "Auto" to allow the adapter to automatically select the optimal channel.
Addressing Driver Issues and Software Conflicts
Outdated or corrupted drivers are a common cause of screen mirroring problems. Regularly updating the drivers for the graphics card and the wireless adapter is essential. As mentioned earlier, downloading drivers directly from the manufacturer's website is often preferable to relying solely on Windows Update. This ensures that the latest and most compatible drivers are installed.
To update the drivers, open Device Manager (search for "Device Manager" in the Start Menu). Expand "Display adapters" and right-click on the graphics card. Select "Update driver" and choose "Search automatically for drivers." Repeat this process for the wireless adapter under "Network adapters." If Windows cannot find updated drivers, visit the manufacturer's website and download the drivers manually. Be sure to download the correct drivers for the specific model of the graphics card and wireless adapter and the version of Windows installed (32-bit or 64-bit).
After downloading the drivers, run the installer. If the installer does not automatically remove the old drivers, consider using a driver uninstaller utility to completely remove the old drivers before installing the new ones. These utilities can help prevent conflicts between old and new drivers. Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) is a popular and effective tool for this purpose. Run DDU in Safe Mode for the best results.
Software conflicts can also interfere with screen mirroring. Certain applications, especially those that manage display settings or network connections, might conflict with Miracast. Try closing any unnecessary applications running in the background to see if it resolves the issue. A clean boot of Windows can help identify if a specific application is causing the problem. A clean boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs. To perform a clean boot, type "msconfig" in the Start Menu and press Enter. In the System Configuration window, go to the "Services" tab, check "Hide all Microsoft services," and then click "Disable all." Go to the "Startup" tab and click "Open Task Manager." Disable all startup items in Task Manager. Restart the computer and try screen mirroring again. If it works after a clean boot, gradually re-enable the services and startup items until the culprit is identified.
Antivirus programs can sometimes interfere with network connections. Temporarily disabling the antivirus software can help determine if it is causing the problem. If disabling the antivirus resolves the issue, configure the antivirus settings to allow Miracast connections or add exceptions for the necessary ports.
Sometimes, the issue arises from a corrupted system file. Run the System File Checker (SFC) tool to scan for and repair corrupted system files. Open Command Prompt as an administrator and type `sfc /scannow` and press Enter. The SFC tool will scan the system files and replace any corrupted files with correct versions. This process may take some time to complete.
Another potential issue is related to the Intel Management Engine Interface (IMEI) driver. An outdated or corrupted IMEI driver can sometimes cause problems with wireless display functionality. Update the IMEI driver from the Intel website or through Device Manager. In Device Manager, look for "System devices" and locate the "Intel Management Engine Interface." Right-click and select "Update driver."
Finally, consider updating the firmware of the Samsung TV. Firmware updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can resolve compatibility issues. Check the Samsung support website for the latest firmware for the specific TV model and follow the instructions to install the update. This usually involves downloading the firmware to a USB drive and then connecting the USB drive to the TV to initiate the update process.

Best Ways To Mirror Windows 10 Samsung Smart Tv

Unable To Miracast Windows 10 Pc Screen Samsung Smart Tv

Solved Why Is Screen Mirroring Not Working On My Samsung Tv

Solved Why Is Screen Mirroring Not Working On My Samsung Tv

How To Use The Pc On Tv Your Samsung Smart Caribbean
Screen Mirroring To Your Samsung Tv

Screen Mirroring To Your Samsung Tv

Screen Mirroring To Your Samsung Tv

How To Screen Mirror Windows 11 A Samsung Smart Tv

Screen Mirroring To Your Samsung Tv








